硅光
常见材料的折射率
- Si:3.882 @632.8 nm
- SiO2:1.457@632.8 nm
- Si3N4:2.023@632.8 nm
- Al2O3:1.770@632.8 nm
技术挑战(Technological Challenges)
- Si的发光非常inefficient,因为它是间接带隙的材料,尽管人们采用各种方法去get around这个缺陷,但是基于Si的laser或者放大器的性能和其他基于其他材料的(比如GaAs或者InP)的还有不小的差距;
- Si的禁带宽度还是太大了,使其不能探测通讯波段的1.3 μm和1.5 μm的光;
- Si没有二阶非线性效应,使得这个材料不能实现electro-optic modulators (EOM);
- The heat dissipated by a laser source on a chip might well be more than is convenient.
目前可能的是办法是制备hybrid devices,由三五族的半导体(直接带隙,有electro-optic properties,比如InP)来实现photonic functions,将其放置在含有各种electronic components的silicon chip上。一类技术基于外延再生长程序,该程序很复杂并且经常大大降低产量。另一种方法是应用复杂的键合工艺将包含波导的硅芯片与提供光学增益的磷化铟芯片结合起来[17]。在这里,需要两个芯片之间的精确对齐。Both technical approaches, leading to silicon hybrid devices, tend to be expensive and are strongly limited in complexity. Therefore, all-silicon solutions, arising from the “siliconization of photonics”, would be more suitable for widespread application. This is also tried for a range of mid-infrared applications such as biochemical sensors.
光纤
单模/多模光纤
【单模光纤】
- 主要特点:
- carriers light pulses along single path. Only the lowest order mode (fundamental mode) can propagate in thr fiber and all high order modes are under cut-off condition (non-propagating)
- 激光器或激光二极管(LD)作为光源
- 常用于长距离传输
-
单模光纤只传输单个脉冲的光,所以单模光纤都采用阶跃型。
- 优点:
- less dispersion
- less degradation
- large information capacity
- core diameter is about 10 μm
- 缺点:
- Expensive to produce;
- 连接两根光纤困难(joining two fibers is difficult)
- launching of light into single mode is difficult
【多模光纤】
- A type of optical fiber mostly used for communication over short distances, such as within a building or on a campus.
- Typical multimode links have data rates of 10 Mbit/s to 10 Gbit/s over link lengths of up to 600 meters.
- Are described by their core and cladding diameters. example: 62.5/125 μm multi-mode fiber
- 发光二极管(LED)或垂直腔面发射激光器(VCSEL)作为光源
- The two types of multi-mode optical fibers are:
- Step index multi-mode optical fibers
- Graded index multi-mode optical fibers
- 阶跃型:在纤芯中沿着光纤轴心以“之”字(zigzag)向前传输。虽然入射光在输入端是以相同的速度同时进行传输,但不同入射角的光线传输路径不同,所以到达终端的时间不同,因而产生时延差,使光脉冲得到展宽,这种称为光纤的模间色散,光纤传输的模式越多,散布的脉冲越多,这大大的限制了光纤的传输容量,所以阶跃型光纤一般用于带宽较窄,小容量短距离通信,比如工控。
- 渐变型:渐变型光纤的纤芯折射率不是常数,纤芯折射率中心最大,沿纤芯半径向往外呈抛物线逐渐减小,光线传输的轨迹近似正弦波。在多模渐变型光纤中,虽然入射光以不同模式在光纤中以不同的路径传输,有的路径长有的路径短,但是在不同折射率下,光的传输速率是不一样的,即靠近轴心的传输速度慢,远离轴心的传输速度快。因此可以选择适当的折射率分布形式,让光线在渐变型光纤中传输时不断进行调整,使不同入射角的光线有大致相同的光程,从而使光线几乎可以同时到达终点,这样就可以解决模间色散的问题,提高光纤带宽,增加传输距离。
- 参考资料:
(1) 阶跃型光纤和渐变型光纤介绍—知乎
(2) ECE 423 Optical Communications-PPT
(3) 一分钟了解光纤、单模光纤、多模光纤—知乎
(4) 单模VS多模,谁才是光纤老大?
(5) 理解单模光纤:基本概念篇—Thorlabs
光波导的模式
Modes in waveguides can be classified as follows:

- 【TEM模】(Transverse electromagnetic modes横电磁模),指的是电场、磁场方向都和传播方向垂直的,我们我们常说的电磁波。
- 【TE模】(Transverse electric modes,横电模),指的是电场方向与传播方向垂直的。
- 【TM模】(Transverse magnetic modes,横磁模),指的是磁场方向与传播方向垂直的。
The wave guiding systems in which an electrostatic field can exist must be able to transmit TEM wave. From Maxwell's equations we can prove that the metal waveguide cannot transmit TEM wave.
参考资料:
(1) Transverse mode-Wiki
(2) Guided Electromagnetic Waves-PPT
(3) TE、TM、TEM模的区别?—知乎
光纤中的损耗
Different Types of Losses in Optical Fiber
- Intrinsic Optical Fiber Losses: Fiber attenuation (signal loss or fiber loss)
- Absorption losses:(主要原因) the light power is absorbed and transferred into other forms of energy like heat, due to molecular resonance and wavelength impurities.
- Dispersion losses:the results of the distortion of optical signal when traveling along the fiber.
- intermodal
- intramodal
- Scattering losses:microscopic variations in the material density, compositional fluctuations, structural inhomogeneities and manufacturing defects.
- Extrinsic Optical Fiber Losses:
- splicing (剪接,拼接)
- patch connections
- bending
- micro bending
- macro bending
参考:Different Types of Losses in Optical Fiber
光纤中的色散
参考资料:
(1) 光纤色散是什么?如何色散补偿?
(2) Chromatic Dispersion—RP-photonics
(3) What is Chromatic Dispersion in Optical Fibers—油管
参考资料:
(1) Silicon Photonics
NV in Diamond
xx
硫系玻璃
磁光效应
法拉第效应
【法拉第效应】(magneto-optic effect)是在介质内光波与磁场的一种相互作用,会造成偏振平面的旋转,which is proportional to the projection of the magnetic field along the direction of the light propagation。
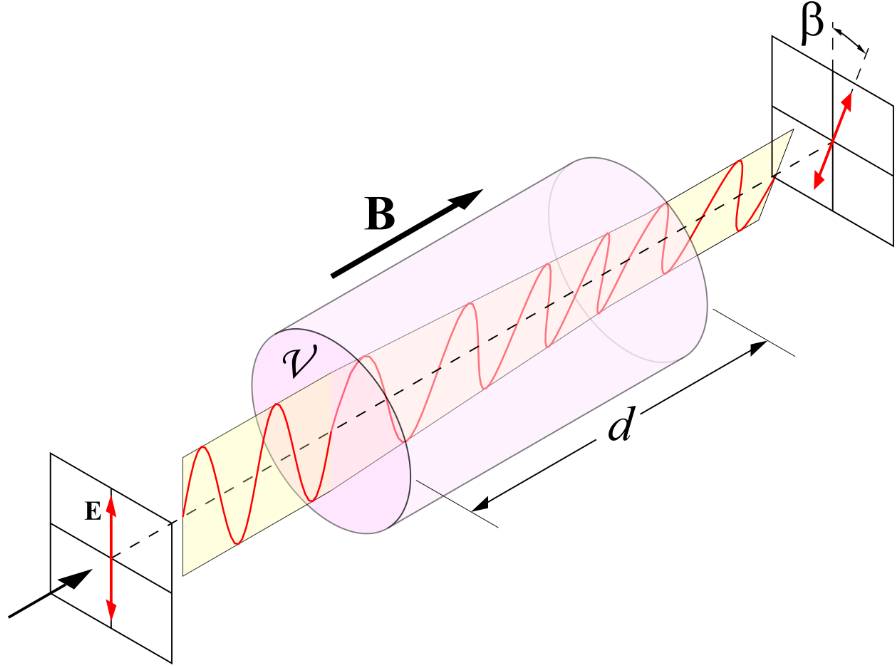 对于透明物质,偏振的旋转角弧与磁场的关系为$$ \beta=\mathcal{V} B d $$其中\(\beta\)是旋转角弧,\(B\)是磁场吵着光波传播方向的分量,\(d\)是光波与磁场相互作用的长度,\(\mathcal{V}\)是物质的韦尔代常数(与材料本质、波长和温度有关)。
对于透明物质,偏振的旋转角弧与磁场的关系为$$ \beta=\mathcal{V} B d $$其中\(\beta\)是旋转角弧,\(B\)是磁场吵着光波传播方向的分量,\(d\)是光波与磁场相互作用的长度,\(\mathcal{V}\)是物质的韦尔代常数(与材料本质、波长和温度有关)。
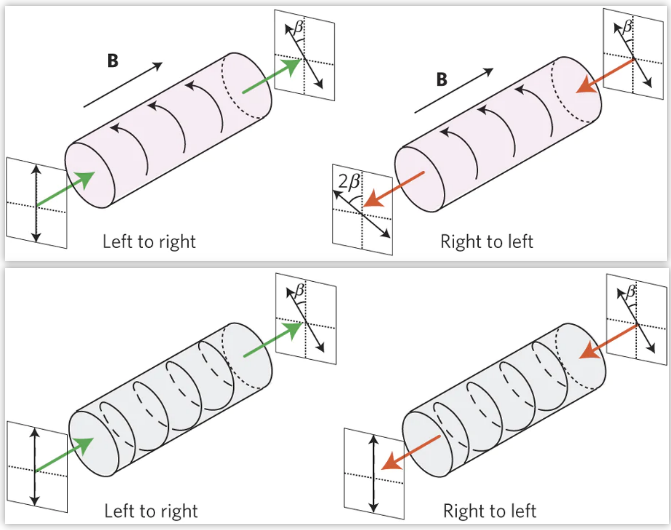
法拉第效应的不可逆 versus optically active crystal Polarization rotation的可逆
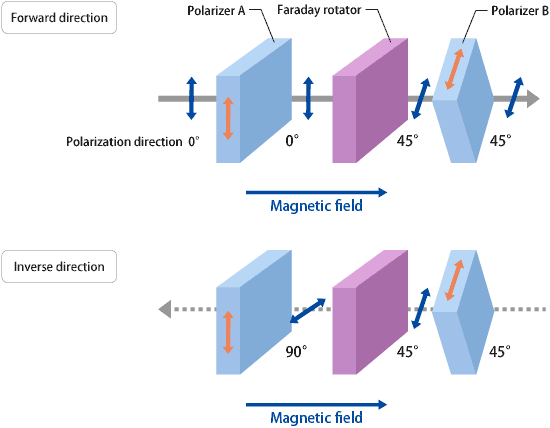
应用:【光隔离器】(Optical Isolator),其工作原理如下图,比如在Erbium-doped Fiber Amplifiers就用到了光隔离器。
磁光克尔效应
xx
参考资料:
(1) FARADAY EFFECT-全-英文 FARADAY EFFECT-全-中文
(2) 材料视界:百年磁光效应的新认识—物理
(3)
其他效应
克尔效应
泡克耳斯效应
xx
VO2
HfO2
斯格明子