Bond Valence Sum(BVS)
BVS概述
$$v_{\mathrm{i}}=\exp \left(\frac{R_{0}-R_{\mathrm{i}}}{b}\right) \quad V=\sum\left(v_{\mathrm{i}}\right)$$where \(R_{\mathrm{i}}\) is the length of a bond between the two given atoms and the bond valence is a measure of the strength of the bond. The parameters \(R_{\mathrm{i}}\) and \(b\) in the equation are compiled or tabulated by I. David Brown. The bond valence has the property that its sum around each atom in a compound is equal to the valence (oxidation state) of that atom. The bond valence is frequently used to validate newly determined crystal structures, but it has many other uses in the analysis and modelling of crystal structures.
参考资料:
(1) Bond valence parameters
(2) Bond valence method-Wiki
(3) Bond-valence parameters obtained from a systematic analysis of the inorganic crystal structure database
(4) 基于键价理论的晶体本征性质经验预测方法与模型及应用-whut博士论文
(5) Bond valence calculation (BVS) 键价计算—知乎
应用-稀土发光领域
例子1:解释Sr和Ba在(Sr,Ba)2SiO4两种格位的占据情况,反映晶体结构的rigidty。
对(Sr,Ba)2SiO4来说,存在10配位的比较大的Sr/Ba1格位,还有9配位的较小的Sr/Ba2格位。作者首先(应该是结构精修)计算了一系列固溶体的Refined occupancies,结果表明Sr倾向于占据更小的Sr/Ba2格位,Ba倾向于占据更大的Sr/Ba1格位。基于初始的BVS计算,Sr1是highly underbonded,Ba2是highly overbonded,这个结果和Refined occupancies的计算结果一致。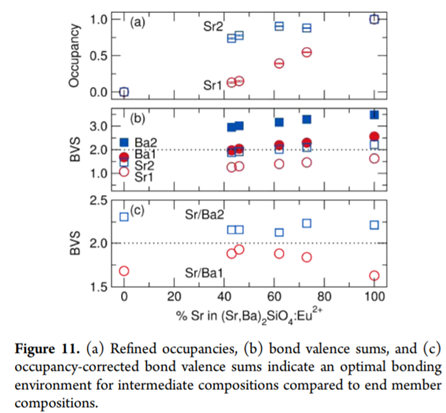
然后基于这个和BVS,和Refined occupancies,重新计算了两个格位的BVS。The end member compositions cause one site to be overbonded and one site to be underbonded, while the intermediate compositions with varying Sr/Ba ratios are able to balance this and achieve an optimized bonding network with a BVS close to +2 for both sites. This indicates that the intermediate compositions form a highly rigid crystal structure, which will have an influence on the thermal stability of the photoluminescence. 作者后续用测试了固溶样品的德拜温度,也是中间相的德拜温度最高,但是基于DFT计算的结果和测试结果矛盾。
例子2:Sc在Ga2O3中占据Ga1还是Ga2格位?BVS计算结果对应于杂相的出现?
在Ga2−xScxO3:Cr3+中,也是存在两种Ga的格位,Sc的引入也会导致两个格位BVS的变化。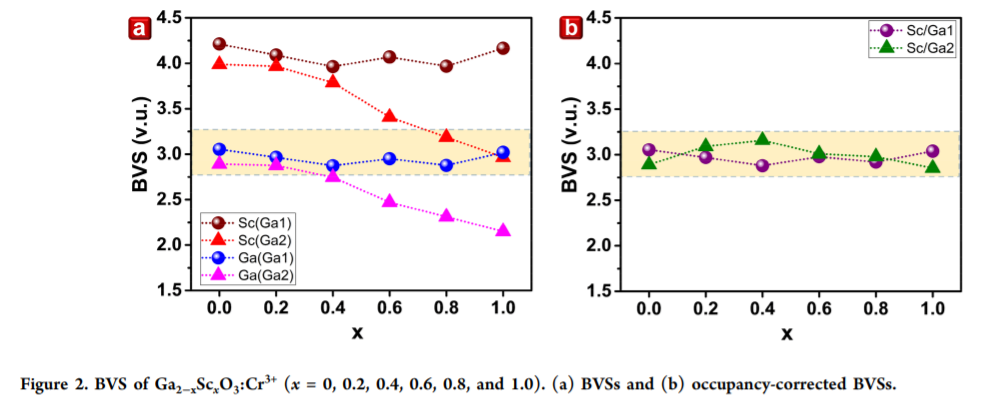 (1) Sc(Ga2)的BVS随着Sc的引入而越来越接近+3,which is not the case for Sc(Ga1),因此说明Sc更倾向于占据Ga2格位。
(1) Sc(Ga2)的BVS随着Sc的引入而越来越接近+3,which is not the case for Sc(Ga1),因此说明Sc更倾向于占据Ga2格位。
(2) 当x大于1.2的时候,Ga的某一个格位的BVS计算值远小于3,也就是处在一个非常underbonded,结构不够rigidity,换句话说就是不稳定,此时的XRD数据也表明了杂相的出现。
(3) 基于Rietveld refinement的格位占据结果,占据概率的改变可以balance BVS的不平衡。For all the samples, changing the Sc3+/Ga3+ ratio between the Ga1 and Ga2 sites can balance the deviation in their BVS value. Neither Sc/Ga(Ga1) nor Sc/Ga(Ga2) is highly overbonded or underbonded. The occupancy-corrected BVS values are closed to +3 throughout the entire series. This finding indicates that Ga2−xScxO3:Cr3+ can have a rigid structure, which further affects its thermal stability.
例子3:解释CsNa2K(Li3SiO4)4中掺杂Ce3+和Eu2+巨大的发光差异和稳定性差异
Ce3+掺杂的样品在日常环境下的强度衰减很弱,但是Eu2+掺杂的样品衰减很强(放置时间长会变成amorphous)。这说明site stability was improved to a greater extent by the Ce3+ doping than by the Eu2+ doping, which enhanced the chemical stability of the host. 
基于结构精修,Ce3+掺杂的样品中,Na–O and K–O 的键长变短了,但是Eu2+掺杂的样品键长没有变化。Furthermore, BVS calculations were performed to determine the ideal oxidation states of activator-substituted sites (Na and K) of the as-synthesized samples. Upon Ce3+ doping, the oxidation states of the Na and K sites achieved an ideal value of 1 (increasing from 0.67 and 0.8, respectively). In contrast, for the K and Na sites, the oxidation states remained at 0.7 and 0.8, respectively, in the case of Eu2+ doping. Overall, Ce3+ doping in CNKLSO can induce greater structural changes than Eu2+ doping, which probably leads to an unprecedented chemical stability for CNKLSO:Ce3+ compared with CNKLSO:Eu2+.
例子x:
应用-电化学领域
例子1:BVS-DMs来反映Mg离子plausible diffusion pathways。
Using 3D bond valence sum difference maps (BVS-DMs), the absolute values of the difference |Δv| between the calculated valence of the magnesium ion at each point on a 3D grid within the unit cell and the ideal valence of 2 are plotted as isosurfaces, such that the plausible diffusion pathways can be graphically visualized, where points less than 1.6 Å away from the oxygen atoms were excluded for the calculation.
The BVS-DMs are generally used to find plausible locations for intercalated ions and to probe ion conduction pathways in inorganic materials. Thus, a threedimensional (3D) BVS-DM calculation was performed using the crystallographic information derived from the XRD Rietveld refinement.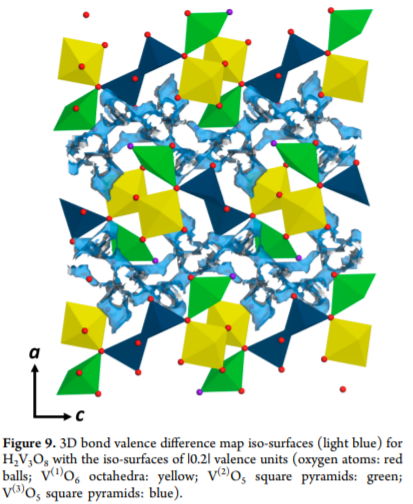
The figure shows BVS-DM isosurfaces at |Δv| = 0.2 valence units (v.u.) for Mg ions. Possible magnesium-ion diffusion pathways are noted within the interlayer, providing additional support for the electrochemical magnesium intercalation into H2V3O8.
实现BVS计算的工具